Techno science
miércoles, 20 de abril de 2011
sábado, 9 de abril de 2011
CLUES TO EARTH"S PAST
Fossil:
are the remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organism.
Permineralized:
are fossils in wich the spaces in side are filled with minerals.
Carbon film:
is a thin carbon residue is left, forming a silhouette of the original organism.
Mold:
the hard part of a might decay or dissolve, leaving behind a cavity in the rock.
Cast:
mineral-rich water or other sediment might enter the cavity, form a new rock, and produce a copy.
Index Fossil:
are the remains of especies that existed on earth for relatively periods of time.
Principle super Deposition:
in undisturbed of rocks, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the rocks become progressively younger toward the top.
Relative Age:
it age comparison to other things.
unconformity:
gaps in rock sequences.
Absolute age:
is the age, in years, of arock or other object.
Radioactive decay:
isotopes are unstable and break down into other isotopes and particles.
half-life:
is the time it takes for half of the atoms in the isotope to decay.
Radiometric dating:
by measuring the radio parent isotope to the daughter product in a mineral knowing the half-life of the parent in many cases you can calculate the absolute age of the rocks.
Uniformitairanism:
states that eath processes occuring today are similar to those occured in the past
martes, 5 de abril de 2011
WATER EROSION AND DEPOSITION
Runoff:
Water that doesn"t soak into the ground or evaporate but intead flows across Earth"s surface.
channel:
Water moving down the same path that create a groove.
Sheet erosion:
occurs when water that is flowing as sheets picks up and carries away sediments.
Drainage basin:
is the area of land from wich stream or river that collects runoff.
Meander:
curve that grows to become a broad.
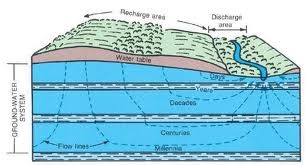
growndwater:
Water that soaks into the ground collects in these pores and empty spaces.
permeable:
that water can pass throught them.
impermeable:
water cannot pass throught them
aquifer:
a layer of permeable rock that lets water move freely.
water table:
are pores in the rocks that are filled with water is the zone of saturation.
spring:
is a water table that is so close to earth surface of water that flows and make a spring.
geyser:
is hot spring that erupts periodically.
cave:
crack in the limestone that enlarge until an undergrownd opening.
Water that doesn"t soak into the ground or evaporate but intead flows across Earth"s surface.
channel:
Water moving down the same path that create a groove.
Sheet erosion:
occurs when water that is flowing as sheets picks up and carries away sediments.
is the area of land from wich stream or river that collects runoff.
Meander:
curve that grows to become a broad.
growndwater:
Water that soaks into the ground collects in these pores and empty spaces.
permeable:
that water can pass throught them.
impermeable:
water cannot pass throught them
aquifer:
a layer of permeable rock that lets water move freely.
water table:
are pores in the rocks that are filled with water is the zone of saturation.
spring:
is a water table that is so close to earth surface of water that flows and make a spring.
geyser:
is hot spring that erupts periodically.
cave:
crack in the limestone that enlarge until an undergrownd opening.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)